shoulder labral tear diagnostic test|speed's test vs o'brien's : solutions Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive . Physical activity can help reduce stress that can cause you to become angry, go for a brisk walk or run when feeling anger escalating.
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB21 de abr. de 2021 · A influenciadora digital Ayarla Souza, de 22 anos, afirma ter sido agredida por vizinhas no condomínio em que mora, em Arujá, por usar short curto. Segundo a jovem, que vive no residencial há .
The O’Brien test is a simple procedure that healthcare professionals use to assess shoulder pain. It can detect a cartilage (labral) tear or an acromioclavicular (AC) . See moreYour shoulder is a large and complex joint. The O’Brien test focuses on your AC joint and labrum. Your AC joint is one of four shoulder joints, where two bones . See more
Healthcare providers who may perform the O’Brien test include: 1. Athletic trainers. 2. Orthopedists(bone and joint specialists). 3. Physical therapists. 4. . See moreSpecial testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive .
Diagnosing Labral Tears of the Shoulder. To evaluate for a possible shoulder labrum tear, a Penn orthopaedic specialist will examine your shoulder, conduct several physical tests to check your range of motion, take a full health history . Take the labrum tear test. There are 4 tests your doctor will conduct on your shoulder that specifically identify a labrum tear. If you respond in pain to any of the test, your test will be considered a pass for that specific test.The purpose of O'Brien's test also known as the Active Compression Test is to indicate potential labral (SLAP Lesion) or acromioclavicular lesions as cause for shoulder pain. [1] [2] .The best tests available to make the diagnosis of a labral tear are magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans or a test called a CT-arthrogram (the latter is a CAT scan preceded by an arthrogram where dye is injected into the shoulder). .
Examination of the shoulder should include inspection, palpation, evaluation of range of motion and provocative testing. In addition, a thorough sensorimotor examination of the upper.
Your doctor may order an MRI scan to determine whether you have a shoulder labral tear or another type of injury causing your symptoms, such as a fracture or torn rotator cuff. The scan .
A shoulder labrum tear is a tear of the labral cartilage that lines the shoulder joint. Get detailed information about labral tears, including SLAP tears and Bankart tears, shoulder labral tear symptoms, diagnostic tests, and . A posterior labral tear is referred to as a reverse Bankart lesion, or attenuation of the posterior capsulolabral complex, and commonly occurs due to repetitive microtrauma in athletes. Diagnosis can be made clinically with . Take the labrum tear test. There are 4 tests your doctor will conduct on your shoulder that specifically identify a labrum tear. If you respond in pain to any of the test, your test will be considered a pass for that specific . Here I demonstrate for you in this video how to perform the O'Brien's Test and talk about what a positive test is and what it means. 👉MedBridge: Online CEUs.
The Clunk Test is used to identify a superior anterior and posterior glenoid labral tear of the shoulder joint. . Diagnostic accuracy of clinical tests for superior labral anterior posterior lesions: a systematic review. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2008;38(6):341-352.This test also called labral crank test or compression rotation test is used to identify glenoid labral tears and assess an unstable superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP) lesions. . load is applied along the axis of the humerus with one hand while the other hand performs humeral rotation while the shoulder is being elevated in the .The results of these physical tests will help your doctor decide if additional testing or imaging of your shoulder is necessary. Imaging Tests. X-rays. X-rays provide clear pictures of dense structures, like bone. The labrum of the shoulder is made . A modification of the active compression test for the shoulder biceps-labrum complex. . Frozen shoulder: Diagnosis and tests. Genovese, Mark. Approach to the exam of the shoulder. Stanford Medicine. By Brett Sears, PT Brett Sears, PT, MDT, is a physical therapist with over 20 years of experience in orthopedic and hospital-based therapy.
A shoulder labral tear is typically diagnosed through a physical exam and imaging tests. Physical Exam. During a physical exam, your doctor asks about your symptoms and physical activities and checks the range of motion, pain, and tenderness in your shoulder. Your doctor may also listen for any grinding noise in the joint as you move your arm .A tear of the front part of the labrum at the bottom of the socket is called a Bankart lesion. This usually happens from an interior shoulder dislocation (a dislocation when the humeral head comes out of the front of the socket). A tear of the labrum can also occur in the back part of the socket. This is called a posterior labral tear. It can .An acetabular labral tear can cause pain if the labrum is torn, frayed, or damaged. . Fitzgerald Test - For assessment of the anterior labrum. The patient's hip is acutely flexed and then extended while internally rotated and in full abduction. . Acetabular labrum tears. Diagnosis and treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1995 Feb;(311):60-8.

Apprehension test performed by bringing the arm in 90 degrees of abduction and full external rotation and patient experiences sense of instability. Relocation test performed by placing examiner's hand on humeral head applying a posterior force on the humeral head. Patient will experience reduction or elimination of sense of instability. Superior labrum anterior to posterior (SLAP) tears are a subset of labral pathology in acute and chronic/degenerative settings. First described in the 1980s, extensive study has followed to elucidate appropriate evaluation and management.[1] Patient-specific considerations and appropriate utilization of both non-surgical and surgical interventions are of the utmost .The data for the proposed Bankart lesion/anterior labral tear tests are presented in Table 4. The TIC that includes that crank test, the apprehension test, . as studies with better statistical data emerge for specific special tests and/or categories of shoulder diagnosis. Special testing should, in the author's opinion, simply should be an .
SLAP Lesion Cluster 1 | Shoulder Assessment. According to a study done by Schlechter et al. (2009), a combination of the Active Compression Test and the Passive Distraction test yields a positive likelihood ratio of 7.0 for 2 positive tests and a negative likelihood ratio of 0.33 for two negative tests. This test cluster therefore has moderate clinical value to confirm or rule out .Shoulder labrum tears may occur: Within or along the edge of the glenoid labrum: most frequent type of glenoid labrum tear, particularly over the age of 40.May not cause any noticeable symptoms; Where the biceps tendon .
speed's test vs o'brien's
special tests for shoulder labrum
Shoulder Labral Tear Treatment. Find a Doctor and Specialists. Make an Appointment. Contents. . Providers use the following tests to diagnose SLAP tears and determine treatment: Physical examination. Your doctor will check your arm and shoulder range of motion and strength.
Explanation of O'Brien's Test in orthopedic shoulder examination including involved tissues, test postion, test movement, etc. plus video demonstration. . Pain over the acromioclavicular joint (a-c joint) indicates pathology at that joint while pain felt ‘deeper’ in the shoulder is more indicative of glenoid labrum pathology. In the event . The glenoid labrum is integral to shoulder stability and can be difficult to assess clinically. Whilst it is a single anatomical structure, damage to different regions results in very different clinical manifestations. A large number of provocative tests have been described, all of which initially purport to have excellent diagnostic accuracy.
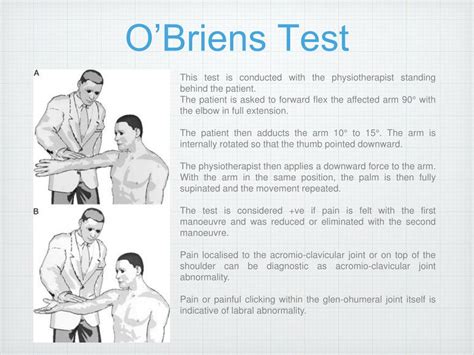
shoulder labrum tear pain location
Rosas et al. (2017) have conducted a literature review and have come up with a test cluster. They found that the uppercut test combined with tenderness to palpation of the long head of the biceps had the highest accuracy to diagnose pathology of the proximal biceps with a sensitivity of 88.3% and a specificity of 93.3%. Although accuracy seems to be high, this combination has not been .
positive shoulder labral tear test
The prerequisite for any treatment in the shoulder region of a patient with pain is a precise and comprehensive picture of the signs and symptoms as they occur during the assessment and as they existed until then. Because of its many structures (most of which are in a small area), its many movements, and the many lesions that may occur either inside or outside the joints, the .The physical examination of the shoulder should include a standardized exam approach as well as a series of special tests to help diagnose the cause of the patients pain. In general, a thorough physical examination will include inspection, palpation, active and passive range of motion, strength, neurovascular and special tests.The researchers concluded that physical tests can’t be used to diagnose shoulder pathology and suggested that physical tests be abandoned for figuring out shoulder pain. Let’s take a look at two more studies about physical tests for shoulder labral tears:The glenoid labrum is a fibrocartilaginous complex that attaches as a rim to the articular cartilage of the glenoid fossa. Its role is to deepen and increase the surface area of the glenoid (acting as a static stabiliser of the glenohumeral joint); resist anterior and posterior movement and assist with blocking shoulder dislocation and subluxation at the maximal ranges of motion.
A systematic review with meta-analyses from Symanski et al suggests that for a diagnosis of SLAP tears, direct MR arthrography is the preferred method. In 2012, Cook et al. investigated the diagnostic accuracy of five orthopedic clinical tests for the diagnosis of SLAP lesions among which they included the labral tension test. In patients where .
positive shoulder impingement test
Introduction. Snyder et al. 1 first coined the term SLAP (superior labrum anterior to posterior) lesion in 1990 after identifying the specific pattern of injury to the superior labrum of the shoulder arthroscopically in 27 patients with various shoulder disorders. A SLAP lesion is an injury to the fibrocartilage rim that runs along the margin of the glenoid cavity. 2 Because of the . Depending on the cause and extent of the tear, the surgeon might remove the torn piece of labrum or repair the torn tissue by sewing it back together. Complications of surgery can include infection, bleeding, nerve injury and recurrent symptoms if the repair doesn't heal properly.The results of the current study indicate that a combination of at least three or more positive clinical tests for a shoulder labral tear may be used to confidently diagnose (or rule out) a shoulder SLAP lesion. . Sheridan K Kreulen C Kim S Mak W Lewis K Marder R. Accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging to diagnose superior labrum anterior .
Resultado da 15 de jun. de 2023 · RT @boyfromrio42: Já disponível no onlyfans e onnowplay. . http://Onlyfans.com/dudu_soares 🇺🇸 . http://Onnowplay.com/eduardo_soares 🇧🇷 @OFCMMRJ
shoulder labral tear diagnostic test|speed's test vs o'brien's